How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying and beyond. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its intricate mechanics, adhering to safety protocols, and developing skillful piloting techniques. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies safely and effectively, whether you’re a novice or seeking to refine your existing skills.
From pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced maneuvers and troubleshooting, we’ll cover all aspects of drone operation. We’ll explore the functionalities of various drone components, explain different flight modes, and delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll also discuss important safety regulations and emergency procedures, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any situation.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone and how they work together is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key components, their functions, and their interplay in enabling flight.
Major Drone Components and Their Interactions
A drone’s flight is a coordinated effort of several key components. The propellers, powered by electric motors, generate thrust. The flight controller, the drone’s “brain,” processes data from various sensors (including the GPS and IMU) and adjusts motor speeds to maintain stability and execute commands from the transmitter. The battery provides the power for all these components, while the camera captures aerial footage.
The GPS module aids in navigation and positioning. The transmitter acts as the interface between the pilot and the drone, allowing for control.
Drone Component Specifications
| Component | Specification Example | Performance Characteristic | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | 8 inch, 4-blade, carbon fiber | High thrust, low noise | Different propeller designs affect efficiency and noise levels. |
| Motors | 2204 2300KV brushless motors | High power-to-weight ratio | KV rating indicates motor speed; higher KV means faster rotation. |
| Flight Controller | Pixhawk 4 | Precise flight control, GPS stabilization | Different flight controllers offer varying levels of features and capabilities. |
| Battery | 1500mAh 3S LiPo | Flight time approximately 20 minutes | Battery capacity and type significantly impact flight duration. |
| Camera | 4K, 30fps, 1/2.3″ sensor | High-resolution video and image capture | Camera resolution and sensor size determine image quality. |
| GPS | High-precision GPS module | Accurate positioning and navigation | GPS accuracy impacts the drone’s ability to hold position and follow waypoints. |
| Transmitter | 2.4GHz radio transmitter | Reliable control at long ranges | Frequency and range capabilities are important factors. |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

A thorough pre-flight check is paramount for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting all components, verifying battery levels, and assessing environmental conditions.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a good understanding of airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of how to operate a drone , including pre-flight checks and emergency procedures, it’s essential to dedicate time to thorough learning. Mastering the art of how to operate a drone will unlock its full potential for various applications.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Inspect propellers for damage or debris.
- Check battery levels and ensure they are fully charged.
- Verify transmitter signal strength and connection to the drone.
- Assess wind speed and direction; avoid flying in high winds.
- Check the surrounding area for obstacles and potential hazards.
- Confirm GPS signal acquisition and accuracy.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
Environmental Factors and Pre-Flight Assessment
Environmental conditions significantly impact drone performance and safety. High winds can make controlling the drone difficult, while extreme temperatures can affect battery performance and electronic components. Always check the weather forecast before flying and avoid unfavorable conditions.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are essential for preventing accidents. This section Artikels procedures for both assisted and manual takeoffs and landings, along with hazard mitigation strategies.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
A smooth takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady hand and monitor the drone’s altitude and orientation. Landing should be performed in a similar manner, gradually decreasing throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essential steps, including safety protocols and legal considerations, consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. This will equip you with the knowledge needed to operate a drone safely and effectively.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
- Assisted Takeoff: Many drones offer assisted takeoff features, automatically managing throttle and stability during ascent.
- Manual Takeoff: This requires more skill and involves manually controlling the throttle and orientation during takeoff.
Hazards During Takeoff and Landing and Mitigation
Potential hazards include strong winds, obstacles near the takeoff/landing zone, and unexpected malfunctions. Mitigation involves choosing a safe and open area, carefully assessing wind conditions, and performing thorough pre-flight checks.
Drone Control and Navigation
Understanding basic drone controls and navigation techniques is crucial for safe and efficient operation. This section covers fundamental control inputs and GPS-based navigation.
Basic Drone Controls
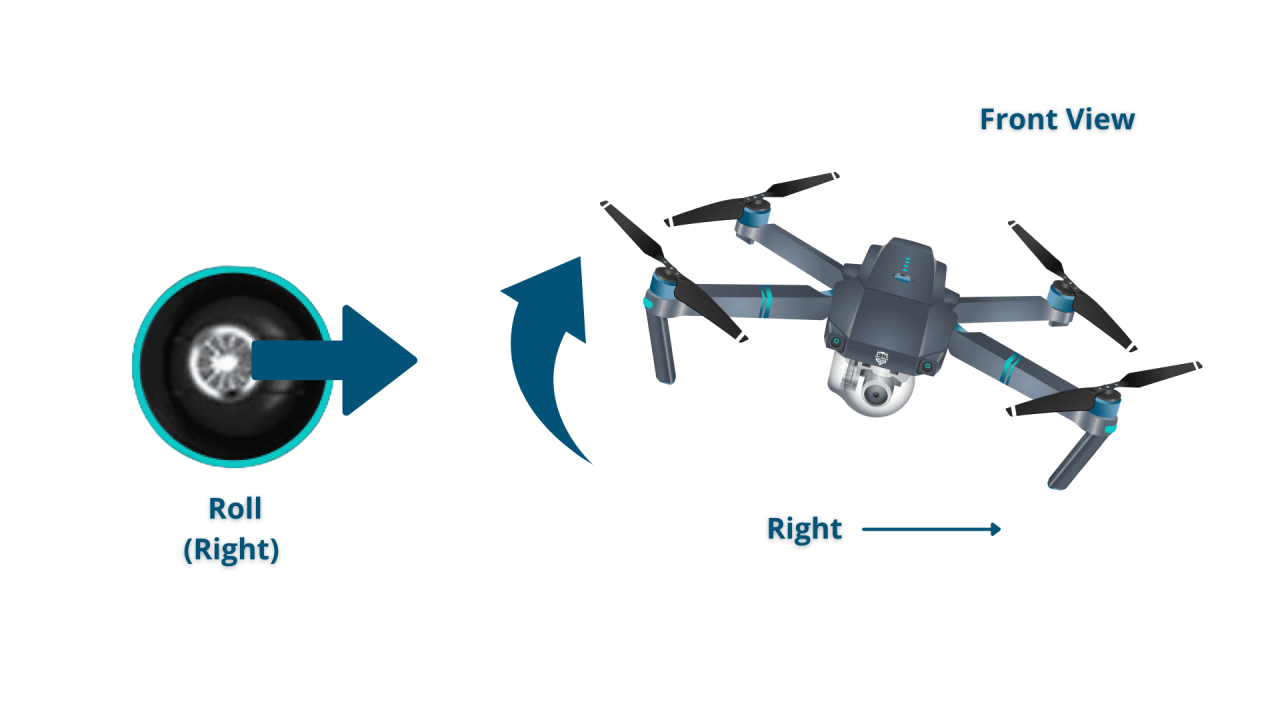
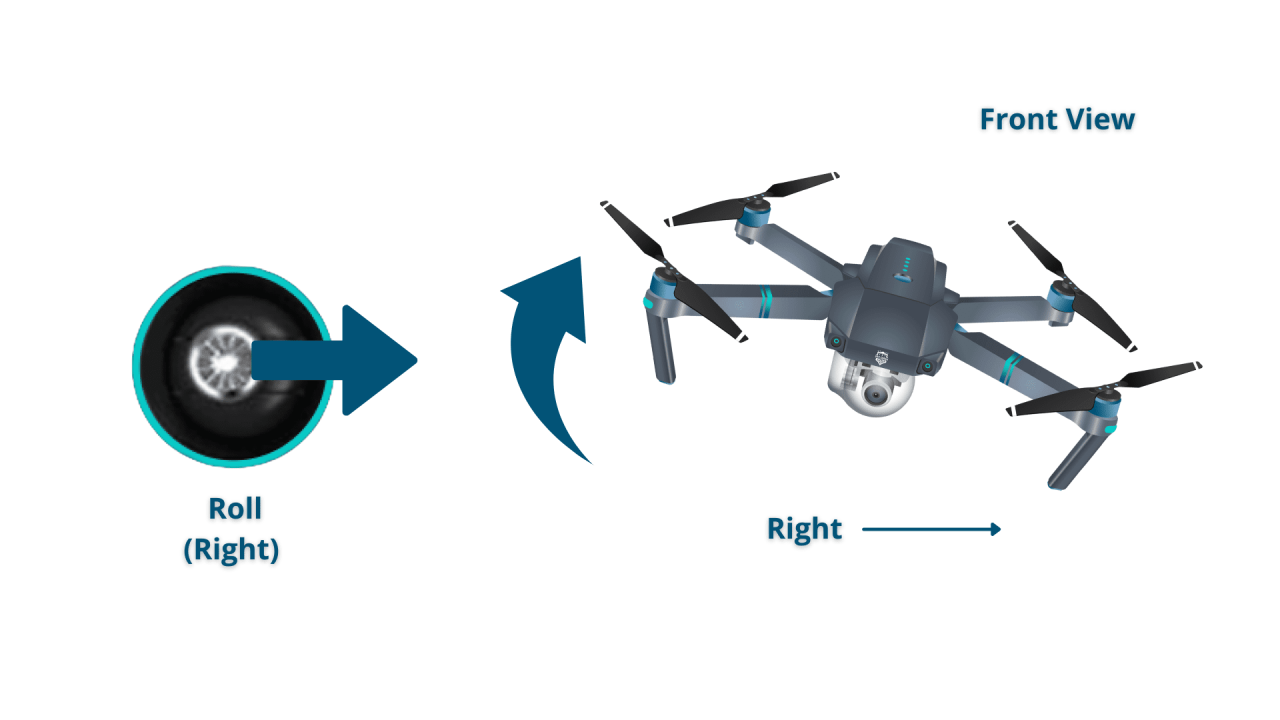
The primary controls are throttle (altitude), pitch (forward/backward), roll (left/right), and yaw (rotation). These controls are typically mapped to sticks on the transmitter.
GPS Navigation and Waypoints
Many drones utilize GPS for precise positioning and navigation. Waypoints can be pre-programmed, allowing the drone to autonomously follow a defined path. This simplifies complex maneuvers and ensures consistent camera angles.
Common Navigation Mistakes and Solutions
- Losing GPS signal: Ensure clear skies and sufficient GPS satellites.
- Improper waypoint planning: Plan waypoints carefully, considering obstacles and wind conditions.
- Overestimating drone capabilities: Fly within the drone’s limitations.
Drone Flight Modes and Settings
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight styles. Understanding and adjusting drone settings optimizes performance and stability.
Flight Modes
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers.
- Cinematic Mode: Prioritizes smooth, stable footage, often with reduced responsiveness.
Adjusting Drone Settings
Drone settings, accessible through the transmitter or mobile app, allow for customization. Adjusting flight limits, camera settings (exposure, ISO, shutter speed), and return-to-home parameters ensures optimal performance.
Effects of Settings on Drone Performance
Altering settings impacts various aspects, including flight stability, responsiveness, and image quality. Experimentation and understanding of these effects are key to achieving desired results.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Mastering drone camera settings and techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Drone Camera Settings
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving desired exposure and depth of field. These settings interact to control the amount of light reaching the sensor, impacting image brightness, sharpness, and noise levels.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving high-quality aerial footage involves careful planning, proper camera settings, and smooth, controlled drone movements. Consider lighting conditions, composition, and subject matter.
Achieving Specific Photographic Effects
- Panning Shots: Smoothly rotating the drone while filming creates dynamic and engaging shots.
- Tracking Shots: Following a moving subject while maintaining a consistent distance and framing.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for ensuring optimal drone performance and longevity. This section provides guidance on cleaning, maintenance, and common problem-solving.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance
Regularly clean the drone’s propellers, body, and camera lens to remove dust and debris. Inspect all components for wear and tear. Store the drone in a dry, protected environment.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions

- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before each flight.
- Signal Loss: Check for interference and ensure a clear line of sight to the drone.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage and replace as needed.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
Establish a regular maintenance schedule, including visual inspections, cleaning, and component checks, to proactively address potential issues and prolong the drone’s lifespan.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe drone operation and adherence to regulations are crucial for responsible flying. This section emphasizes safe practices and legal requirements.
Safe Drone Operation Practices
Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone. Avoid flying near airports, crowded areas, or sensitive infrastructure. Be mindful of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with local laws and obtain necessary permits or licenses before operating a drone. Respect airspace restrictions and privacy concerns.
Potential Risks and Hazards
Potential risks include collisions, damage to property, privacy violations, and injuries. Responsible flying minimizes these risks. Always prioritize safety.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section details procedures for malfunctions, crashes, and emergency landings.
Drone Malfunction During Flight
If a malfunction occurs, attempt to regain control and perform a controlled landing. If this is not possible, activate the return-to-home function (if available) or prepare for an emergency landing.
Recovering a Crashed Drone, How to operate a drone
Assess the damage to the drone and components. Repair or replace damaged parts as needed. Always prioritize safety when recovering a crashed drone.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In an emergency, prioritize a safe landing location, even if it means sacrificing the drone. Try to land in a soft, open area to minimize damage.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced piloting techniques, specialized equipment, and software applications for enhancing drone capabilities.
Advanced Piloting Techniques
Precision hovering, complex maneuvers, and advanced flight modes require practice and skill. Mastering these techniques expands the possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
Specialized Drone Equipment and Accessories
Various accessories enhance drone functionality, including different cameras, gimbals, and flight controllers. Choosing the right equipment depends on specific needs and applications.
Drone Software for Flight Planning and Data Analysis
Software applications facilitate flight planning, autonomous missions, and data analysis from aerial imagery. These tools enhance efficiency and workflow.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience that combines technical understanding with practical skill. By mastering the fundamentals, adhering to safety regulations, and continually refining your techniques, you can unlock the full potential of this versatile technology. Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount, and this guide serves as a foundation for a safe and enjoyable flight experience. Continue to learn, practice, and explore the boundless possibilities that await you in the world of drone technology.
FAQ Compilation: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with intuitive controls and robust safety features.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight and in a safe, open area.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.